When you’re running just a handful of automated tests, life feels good — scripts run smoothly on your local machine, and results arrive in minutes. But as soon as your test suite grows into hundreds or thousands of cases, or you need to validate across multiple browsers and operating systems, local execution slows to a crawl.
That’s when Selenium Grid comes to the rescue. It lets you run tests in parallel across multiple environments. And when you combine Selenium Grid with Docker, you unlock a lightweight, scalable, and consistent test infrastructure — without the pain of managing physical or virtual machines manually.
In this blog, we’ll cover why Dockerized Selenium Grid is better than traditional setups, how its architecture works, a step-by-step setup guide, integration with CI/CD pipelines, common pitfalls, best practices, cloud alternatives, and what’s new in Selenium Grid 4.
Why Dockerized Selenium Grid?
Before Docker, Selenium Grid setups involved installing a central Hub, configuring browser Nodes on separate machines, and keeping drivers updated manually. It worked but was difficult to maintain. Updating browsers often broke compatibility and wasted valuable time.
Docker simplifies this by providing ready-made container images that include browsers, drivers, and node configurations. These containers are portable, consistent, and disposable, making them ideal for test automation setups.
You Might Also Like: automation testing interview questions
Benefits of Dockerized Selenium Grid include:
• Instant setup with minimal commands.
• Consistency across local, staging, and CI environments.
• Isolation of dependencies.
• Simple scalability by running additional containers.
• Reduced maintenance overhead with version-controlled images.
How the Architecture Works
A Dockerized Selenium Grid typically includes:
• A Hub (or Router in Selenium Grid 4) that manages incoming test requests.
• Multiple Nodes (Chrome, Firefox, or Edge) that execute tests.
• A Docker network that ensures smooth communication between Hub and Nodes.
• Automation scripts pointing to the Hub’s endpoint.
Execution flow:
1. Your test script sends a request to the Hub URL.
2. The Hub identifies a free Node.
3. The Node launches the browser, runs the test, and returns results.
4. Results are passed back to your test framework.
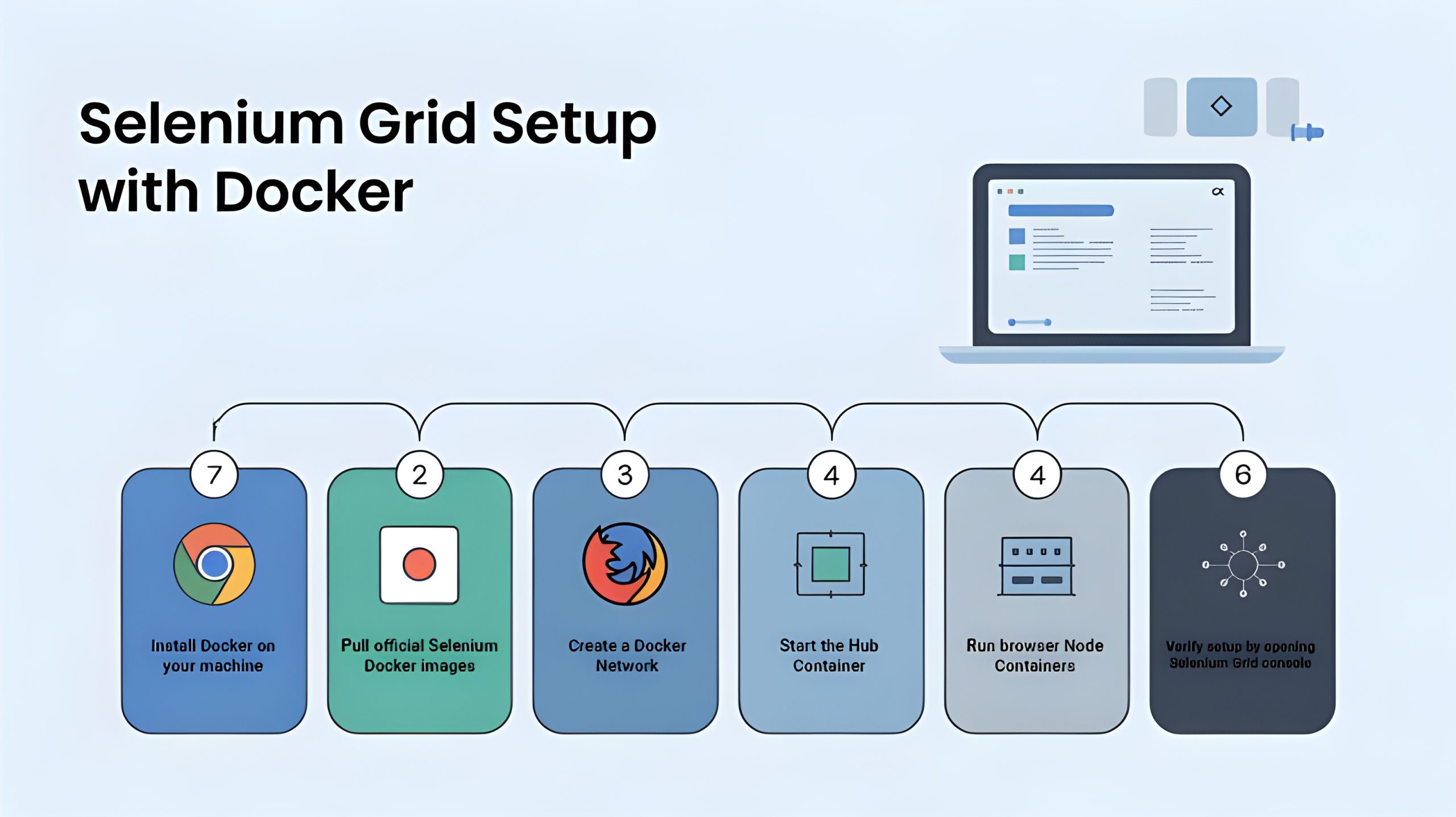
Step-by-Step Setup
Step 1: Install Docker on your machine. For Windows and Mac, use Docker Desktop. On Linux, install via apt or yum.
Step 2: Pull official Selenium Docker images, which include the Hub and browser Nodes.
Step 3: Create a Docker network to allow containers to communicate securely.
Step 4: Start the Hub container and expose it on port 4444.
Step 5: Run browser Node containers (Chrome, Firefox, etc.) and connect them to the Hub.
Step 6: Verify your setup by opening the Selenium Grid console in a browser and checking that Nodes are registered.
Running Tests on the Grid
Once the Grid is up, your test scripts should point to the Hub’s endpoint instead of local browser drivers. The Hub will distribute tests to available Nodes. This makes parallel test execution possible, dramatically reducing execution times when working with large test suites.
Scaling the Grid
Scaling is straightforward with Docker. If your team needs to run dozens of tests simultaneously, you can launch more Node containers. For example, instead of one Chrome Node, you can run five or ten. The Hub automatically balances requests across all Nodes, ensuring optimal utilization of resources.
Using Docker Compose for Simplicity
Managing multiple containers with separate commands is inefficient. Docker Compose allows you to define the Hub and multiple Nodes in a single configuration file. With one command, you can bring up or tear down the entire Grid. This simplifies setup and is the preferred approach for real-world projects.
Integrating with CI/CD
Dockerized Selenium Grid integrates seamlessly into CI/CD pipelines with tools such as Jenkins, GitHub Actions, and GitLab CI. A typical workflow involves:
1. Spinning up the Grid before tests.
2. Running parallel automated tests against the Grid.
3. Shutting down containers once execution finishes.
This ensures a clean, reproducible environment for every test run, avoiding flakiness from stale sessions.
Best Practices for Dockerized Selenium Grid
- Always match browser and driver versions to prevent errors.
- Configure parallel execution in your test framework (TestNG, JUnit, PyTest).
- Assign resource limits to containers to prevent bottlenecks.
- Enable VNC to watch tests visually in real-time when debugging.
- Clean up unused containers and images regularly to free disk space.
- Monitor resource usage to avoid overloading your system during parallel runs.

Common Errors and Fixes
- SessionNotCreatedException occurs when the browser and driver versions don’t match. Update to compatible versions.
- Nodes not registering with the Hub often happen due to incorrect hostnames. Double-check container names.
- Test timeouts may indicate limited system resources. Increase Docker’s CPU or RAM allocation.
What’s New in Selenium Grid 4 with Docker?
Selenium Grid 4 introduced major improvements:
• Unified Hub — no need for separate Hub and Node jars.
• Observability support — built-in metrics and logging for better monitoring.
• Native Kubernetes and Docker Swarm support, with official Helm charts.
• Session Queues that hold requests instead of failing immediately when no Nodes are available.
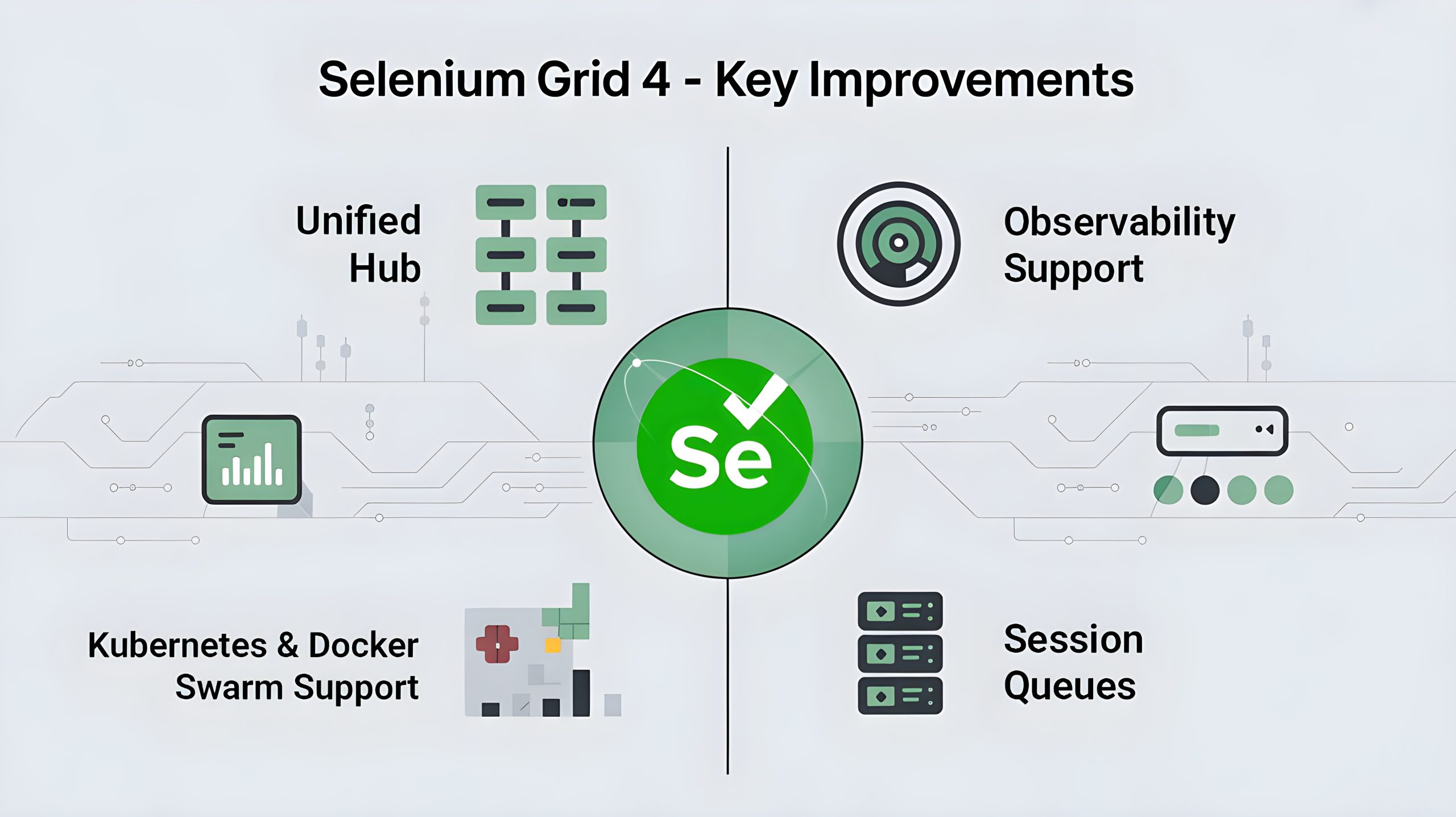
These updates make Dockerized Selenium Grid 4 a strong choice for enterprise-scale test automation.
Cloud Alternatives vs Dockerized Grid
| Aspect | Dockerized Selenium Grid | Cloud Testing Platforms |
| Setup | Manual setup with Docker commands/Compose | Instant setup with provider tools |
| Cost | Low (infrastructure only) | Subscription-based, higher recurring costs |
| Scalability | High, needs infra management | Very high, managed by provider |
| Debugging | Local VNC/debug tools | Provider dashboards & tools |
| Flexibility | Full control of environment | Limited to provider features |
Final Thoughts
Dockerized Selenium Grid is a transformative tool for scaling automated testing. It enables teams to run tests across multiple browsers and operating systems with ease, while dramatically reducing execution times. Its integration with CI/CD, scalability, and flexibility make it a must-have for modern test automation strategies.
For small teams, it provides simple cross-browser validation. For large organizations, it ensures consistent, maintainable, and scalable testing pipelines. Once you experience its efficiency, it becomes hard to imagine going back to traditional setups. In fact, Dockerized Grids have become a game-changer for software testing with Selenium, helping QA teams achieve faster feedback and higher reliability across projects.
We Also Provide Training In:
- Advanced Selenium Training
- Playwright Training
- Gen AI Training
- AWS Training
- REST API Training
- Full Stack Training
- Appium Training
- DevOps Training
- JMeter Performance Training
Author’s Bio:

As a Senior SDET with 8+ years in testing and development, I build scalable automation platforms ensuring quality at speed. Passionate about mentoring and innovation, I equip teams with real-time solutions and high-impact frameworks, driving excellence through continuous learning. Let’s shape the future of quality engineering together.
Dilipkumar Rajendran
Senior SDET | Playwright & Selenium Expert