In the modern IT landscape, quality is just as important as speed. Businesses demand software that not only meets customer needs but also works seamlessly in production. For Quality Assurance (QA) professionals, having a strong grasp of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is crucial. Understanding the life cycle of software development helps testers align their strategies with development goals, ensuring every release is efficient, reliable, and user-focused.
The SDLC for software development provides a structured approach to building applications. It defines how software should be planned, built, tested, and maintained. For QA teams, this means knowing exactly where testing fits into the bigger picture and how to contribute at every stage.
What is SDLC?
The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a systematic process used to design, develop, test, and deploy high-quality software. It outlines a step-by-step framework that guides teams through the SDLC development journey, ensuring consistency and minimizing risks.
In simple terms, the SDLC software development framework helps teams answer three key questions:
- What needs to be built? (requirements)
- How will it be built? (design and coding)
- How will we ensure it works? (testing and deployment)
By following an SDLC, organizations can manage time, cost, and quality more effectively. For QA professionals, understanding SDLC means being able to contribute to every stage of the software development SDLC, from validating requirements to supporting post-deployment maintenance.
Other Helpful Articles: selenium interview questions
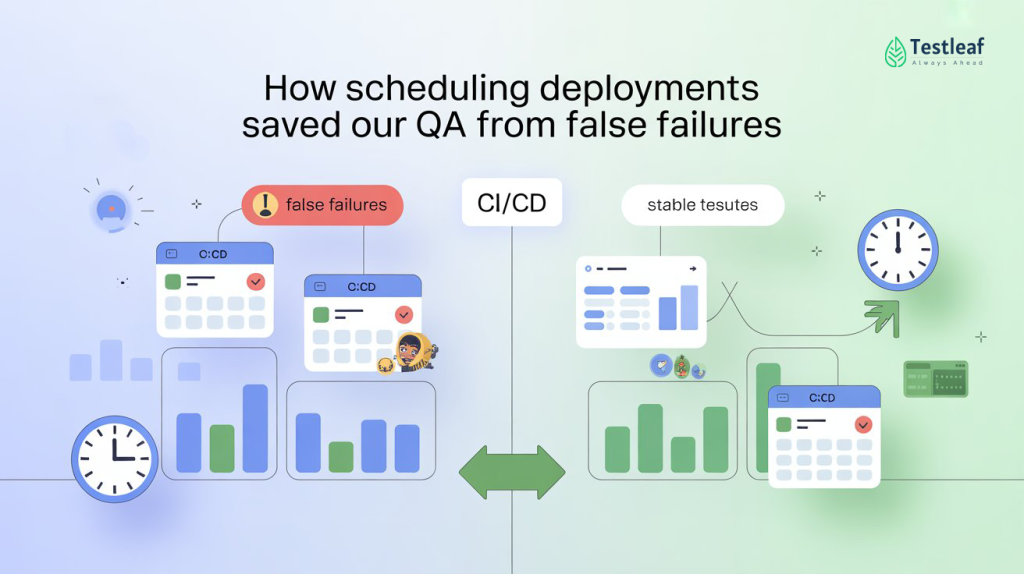
Software Development Life Cycle Phases
The software development life cycle phases are the backbone of any SDLC framework. Each phase has its own objectives and deliverables, creating a roadmap for developers and testers alike.
- Requirement Analysis – Business analysts gather customer requirements, and QA professionals validate these for clarity, completeness, and testability.
- Design – Architects create the system’s blueprint. QA teams ensure that design choices are aligned with performance, security, and usability needs.
- Development – Code is written according to specifications. QA professionals begin preparing test data, test cases, and automation frameworks.
- Testing – QA teams validate functionality, performance, and security. This phase ensures the product meets quality standards before release.
- Deployment – The software is released into production. QA teams often perform smoke or sanity testing in live environments.
- Maintenance – Post-deployment, QA supports updates, bug fixes, and regression testing to keep the application stable.
By actively engaging in each stage, QA professionals move beyond defect detection—they become quality partners in the SDLC lifecycle.
You Might Also Like: api testing interview questions
Software Development Life Cycle Processes
The software development life cycle processes refer to the practices and methodologies followed to ensure success. These are not just technical activities but also procedural elements that bring consistency and quality.
- Requirement Validation – Ensuring all requirements are testable and measurable.
- Design Review – Collaborating with architects to identify risks early.
- Code Quality Assurance – Conducting code reviews, static analysis, and maintaining coding standards.
- Testing Strategy – Combining manual testing with automation for faster coverage.
- Defect Management – Logging, tracking, and resolving bugs in a structured manner.
- Release Management – Coordinating deployments with minimal risk.
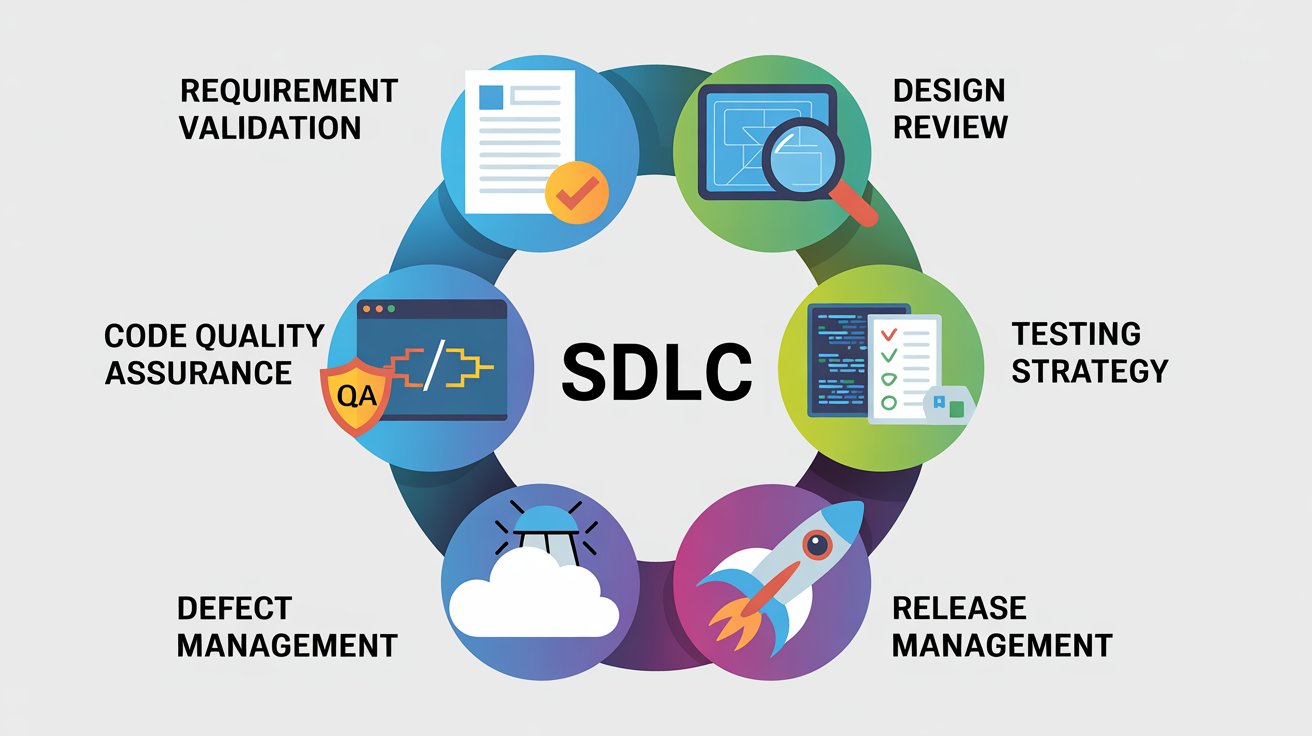
For QA, following these life cycle development processes ensures that testing is not an afterthought but an integral part of the delivery pipeline.
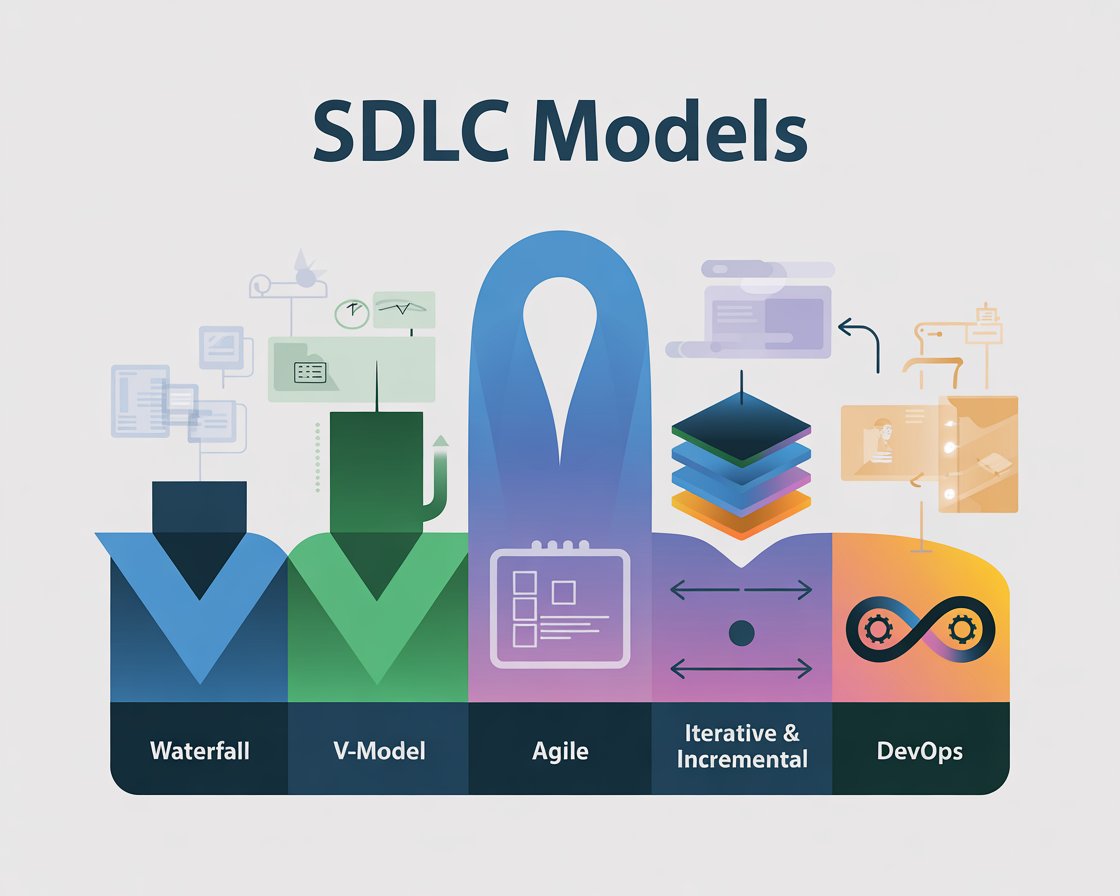
Software Development Life Cycle Model
There isn’t just one software development life cycle model—different models suit different types of projects. QA professionals must adapt their testing approach depending on which model is in use.
- Waterfall Model – Sequential and rigid. Testing happens after development, making defect detection late but predictable.
- V-Model – Testing activities are mapped to each development phase, creating a structured validation process.
- Agile Model – Iterative and flexible. QA collaborates with developers continuously, ensuring faster feedback loops.
- Iterative & Incremental Models – Features are built and tested in cycles, allowing early feedback and gradual improvements.
- DevOps/Continuous Delivery – Testing integrates with CI/CD pipelines, making automation and monitoring critical for quality.
Choosing the right software development SDLC model can drastically affect how QA contributes to project outcomes. For instance, in Agile and DevOps, testers play a proactive role in preventing defects rather than just finding them.
Why SDLC Knowledge Matters for QA Professionals
QA professionals who understand the SDLC development framework gain several advantages:
- They can predict where issues may occur and prepare testing strategies accordingly.
- They collaborate effectively with developers, business analysts, and stakeholders.
- They align testing activities with business goals, reducing bottlenecks in delivery.
- They contribute to risk management by identifying gaps early in the SDLC software development journey.
Simply put, knowledge of SDLC enables QA professionals to elevate their role from testers to quality advocates.
Conclusion
For QA professionals, mastering the SDLC lifecycle isn’t optional—it’s essential. From understanding requirements to maintaining live systems, every phase and process offers opportunities for testers to ensure software quality. Whether working with Agile, Waterfall, or DevOps, QA teams must align with the chosen software development life cycle model to add maximum value.
If you’re aspiring to become a skilled QA professional, enhancing your knowledge through structured learning is the best next step. Enrolling in a Software testing course online will not only sharpen your SDLC understanding but also give you practical expertise to thrive in real-world projects.
FAQs
Q1: What is the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) in QA?
The SDLC is a structured process of planning, designing, developing, testing, and maintaining software. For QA, it provides a framework to align testing with development at every stage.
Q2: Why is SDLC important for QA professionals?
It helps QA predict issues, design effective test strategies, collaborate with developers, and ensure business goals align with software quality.
Q3: Which SDLC model is best for QA teams?
Agile and DevOps are most QA-friendly because they allow continuous collaboration, early defect detection, and automation-driven quality.
Q4: How does QA contribute in SDLC phases?
QA validates requirements, reviews designs, prepares test cases, executes tests, manages defects, and ensures quality in deployment and maintenance.
Q5: How can I learn SDLC as a QA professional?
You can master SDLC concepts through structured learning, hands-on projects, and enrolling in a software testing course online that covers QA’s role in different SDLC models.
We Also Provide Training In:
- Advanced Selenium Training
- Playwright Training
- Gen AI Training
- AWS Training
- REST API Training
- Full Stack Training
- Appium Training
- DevOps Training
- JMeter Performance Training
Author’s Bio:

Content Writer at Testleaf, specializing in SEO-driven content for test automation, software development, and cybersecurity. I turn complex technical topics into clear, engaging stories that educate, inspire, and drive digital transformation.
Ezhirkadhir Raja
Content Writer – Testleaf