Introduction: Why Testing Models Deserve Your Attention
In modern software projects, testing is not an afterthought. It is a decision-making process that starts even before the first line of code is written.
Yet many beginners struggle because they learn what to test but not how testing fits into development. This gap is exactly where software testing models play a vital role.
This guide explains 10 essential software testing models in a way that is:
- Easy to understand
- Structured logically
- Aligned with real project workflows
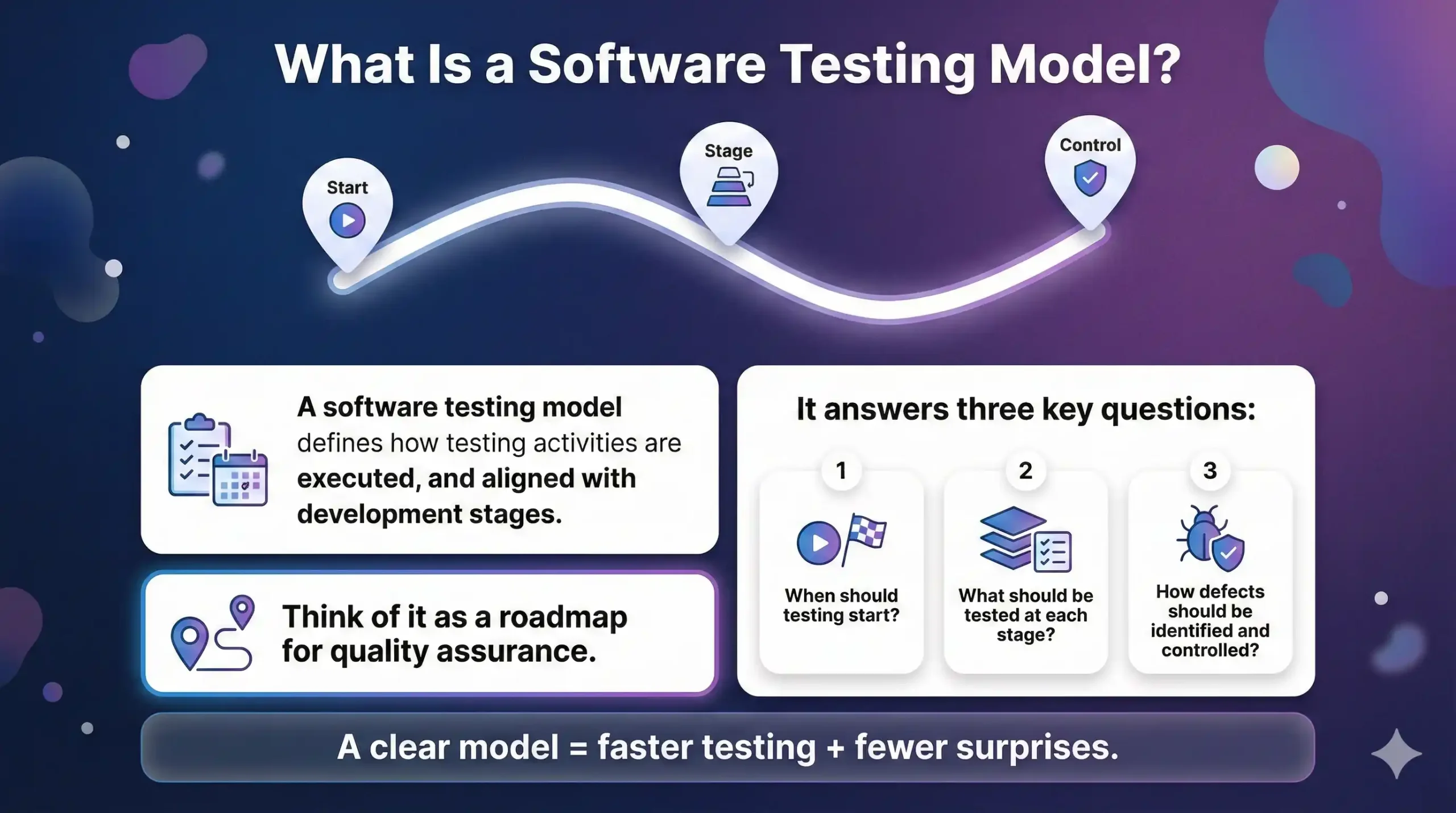
What Is a Software Testing Model?
A software testing model defines how testing activities are planned, executed, and aligned with development stages.
Think of it as a roadmap for quality assurance.
It answers three key questions:
- When should testing start?
- What should be tested at each stage?
- How defects should be identified and controlled?
Different projects require different models. That is why understanding multiple models is more valuable than memorizing one.
1. Waterfall Testing Model
The Waterfall model follows a strict linear flow. Development moves step by step—from requirements to design, development, testing, and release.
How testing works here
Testing begins only after development is completed. Testers validate the final product against documented requirements.
Why it is still used
- Requirements are clearly defined
- Documentation is mandatory
- Regulatory projects prefer predictability
Why it fails in modern projects
- Defects are found very late
- Requirement changes are costly
- No early feedback loop
2. V-Model (Verification and Validation Model)
The V-Model improves Waterfall by integrating testing early.
How testing works here
Each development phase has a corresponding testing phase.
For example:
- Requirements → Acceptance Testing
- Design → System Testing
- Coding → Unit Testing
Key advantage
Test planning starts early, reducing ambiguity and missed requirements.
Limitation
Still rigid. Changes are difficult once the project starts.
3. Agile Testing Model
Agile testing runs continuously, alongside development.
How testing works here
Testing is embedded into every sprint. Testers collaborate closely with developers and product owners.
Testing focus
- Frequent feedback
- Automation-ready test cases
- User stories as test inputs
Common challenges
- Limited documentation
- Requires strong communication skills
4. Iterative Testing Model
In this model, software is built and tested in repeated cycles.
How testing works here
Each iteration includes planning, development, testing, and review. Defects are fixed before moving forward.
Why teams choose it
- Early visibility of the product
- Better risk control
- Continuous improvement
Drawback
Needs careful planning to avoid scope creep.
5. Spiral Testing Model
The Spiral model is risk-driven.
How testing works here
Each spiral loop focuses on identifying risks, developing solutions, and validating them through testing.
Where it excels
- Large enterprise systems
- High-risk applications
- Complex architectures
Why it’s not common
Requires experienced teams and higher budgets.
6. Incremental Testing Model
Software is delivered and tested in functional increments.
How testing works here
Each module is tested individually before integration.
Strength
- Faster defect isolation
- Early feature validation
Limitation
Integration issues may appear later if dependencies are ignored.
7. Big Bang Testing Model
All modules are integrated and tested at once.
How testing works here
There is no structured test planning. Testing begins only when development ends.
Why it is risky
- Difficult defect tracing
- No early quality signals
When it’s acceptable
Very small or experimental projects only.
8. DevOps Continuous Testing Model
Testing is integrated into CI/CD pipelines.
How testing works here
Automated tests run at every stage—build, deploy, and release.
Why it matters in 2026
- Faster releases
- Higher reliability
- Production-ready quality
Requirement
Strong automation skills and tool maturity.
9. Risk-Based Testing Model
Testing is prioritized based on business impact and failure probability.
How testing works here
Critical features are tested first. Low-risk areas receive limited coverage.
Why companies use it
- Saves time and cost
- Aligns testing with business goals
Skill needed
Domain knowledge and analytical thinking.
10. Model-Based Testing (MBT)
Tests are derived from system behavior models.
How testing works here
Test cases are auto-generated from flow diagrams or state models.
Best suited for
- Complex workflows
- Automation-heavy environments
Limitation
High initial effort and learning curve.
How to Choose the Right Testing Model
Instead of asking “Which model is best?”, ask:
- How stable are the requirements?
- How frequently do we release?
- What is the risk of failure?
- How mature is the team?

Experienced testers do not follow models blindly—they adapt them.
Why Understanding Testing Models Boosts Your Career
For beginners, testing models:
- Build strong fundamentals
- Improve interview performance
- Enable smarter test planning
For intermediate testers, they:
- Improve automation strategy
- Strengthen collaboration with developers
- Support leadership and decision-making roles
Final Thoughts: Quality Is a Strategy, Not a Phase
In 2026, software quality is no longer optional.
Testing models are not academic concepts—they are decision-making tools.
By mastering these 10 software testing models, you move beyond simply executing predefined test cases and begin to think like a quality engineer. You start understanding why a feature should be tested, when testing should begin, and how quality decisions impact business outcomes. This shift transforms testing from a task-based role into a strategic responsibility, enabling you to collaborate effectively with developers, product owners, and stakeholders.
For learners who want to build this mindset through structured guidance and hands-on practice, enrolling in a software testing course in chennai can provide real-world exposure that reinforces these concepts. This evolution in thinking is what clearly separates average testers from in-demand professionals in today’s competitive QA market.
FAQs
1. What is a software testing model?
A software testing model is a structured approach that defines how testing activities are planned, executed, and aligned with each stage of the software development lifecycle.
2. Why are software testing models important?
Testing models help teams detect defects early, reduce cost, improve software quality, and ensure testing is aligned with business and development goals.
3. Which software testing model is best for beginners?
The V-Model and Agile testing model are best for beginners because they clearly link development stages with testing activities and encourage early defect detection.
4. What is the difference between Agile and Waterfall testing models?
Waterfall testing follows a linear approach with testing at the end, while Agile testing is continuous and integrated into every development sprint.
5. Are software testing models still relevant in 2026?
Yes. With DevOps, CI/CD, and AI-driven development, testing models have evolved and are more critical than ever for maintaining speed and quality.
6. How do testing models help in a QA career?
Understanding testing models improves test planning, communication with developers, interview performance, and readiness for automation and leadership roles.
We Also Provide Training In:
- Advanced Selenium Training
- Playwright Training
- Gen AI Training
- AWS Training
- REST API Training
- Full Stack Training
- Appium Training
- DevOps Training
- JMeter Performance Training
Author’s Bio:

Content Writer at Testleaf, specializing in SEO-driven content for test automation, software development, and cybersecurity. I turn complex technical topics into clear, engaging stories that educate, inspire, and drive digital transformation.
Ezhirkadhir Raja
Content Writer – Testleaf







