As a QA engineer, one of the most critical responsibilities is ensuring that new changes don’t break existing functionality. This is where regression testing comes in. A regression suite acts as the safety net, catching defects before they reach production. However, I quickly learned that a regression suite is only as valuable as its stability. Flaky tests, inconsistent environments, and poor maintenance can render even the most extensive suite unreliable.
Over the years, I’ve worked on building stable, reliable regression suites that not only detect defects but also integrate seamlessly into CI/CD pipelines. Here’s a complete guide from my perspective on achieving a stable QA regression suite.
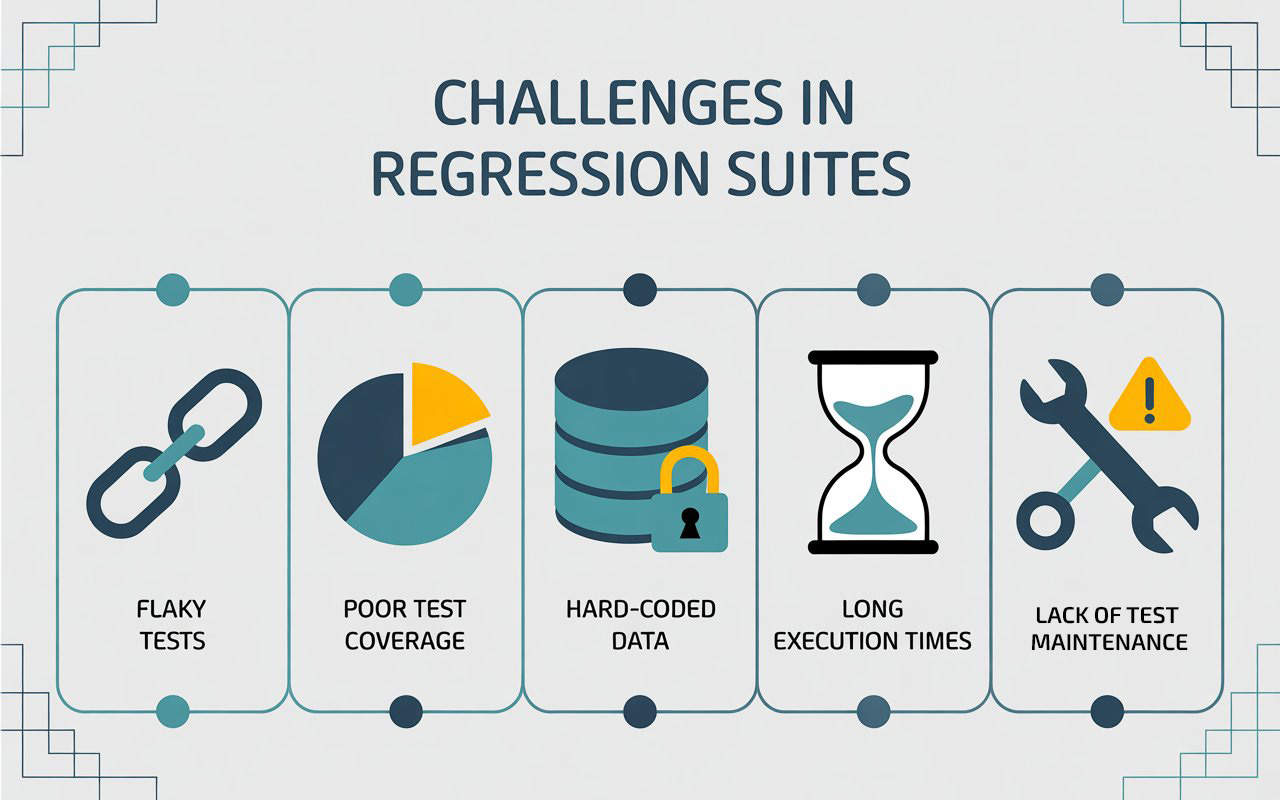
Understanding the Challenges
Before tackling stability, it’s important to understand the common issues that plague regression suites:
1. Flaky Tests
Tests that fail intermittently due to timing issues, network latency, or environmental instability create noise. They erode confidence in the suite and make it hard to trust pipeline results.
2. Poor Test Coverage
Regression suites often cover happy paths extensively but miss critical edge cases. This leads to false confidence, where tests pass but real defects slip into production.
3. Hard-Coded Data
Many legacy regression tests rely on hard-coded inputs. Changes to test data or environments frequently break these tests, causing maintenance headaches.
4. Long Execution Times
As the application grows, regression suites expand. Sequential execution can take hours, slowing down CI/CD pipelines and delaying feedback.
5. Lack of Test Maintenance
Over time, some tests become irrelevant or duplicate others. Without periodic review, suites accumulate technical debt, reducing reliability.
Step 1: Define a Clear Regression Strategy
Stability begins with planning and prioritization. A well-structured regression strategy includes:
- Categorization of Tests: Divide tests into smoke, critical, and full regression sets. Smoke tests validate major functionality quickly, while full regression covers end-to-end scenarios.
- Frequency: Decide which tests run daily, per commit, or per release. This reduces unnecessary load on pipelines.
- Ownership: Assign test ownership to ensure accountability for maintenance and updates.
Step 2: Improve Test Reliability
Reliable tests are the foundation of a stable regression suite. Key techniques include:
Use Explicit Waits Instead of Hard Sleeps
Hard-coded waits slow execution and introduce flakiness. Explicit waits allow tests to proceed only when elements are ready, improving both speed and reliability.
WebDriverWait wait = new WebDriverWait(driver, Duration.ofSeconds(10));
WebElement element = wait.until(ExpectedConditions.visibilityOfElementLocated(By.id(“submitBtn”)));
Isolate Tests
Tests should run independently, without relying on data or state from previous tests. Isolation prevents cascading failures that reduce suite stability.
Parameterize Test Data
Centralized and parameterized test data ensures tests are flexible and reusable, avoiding failures due to outdated or hard-coded values.
Step 3: Optimize Test Coverage
A stable regression suite isn’t just reliable—it also covers critical workflows and edge cases.
- Positive Scenarios: Ensure happy paths are covered to verify core functionality.
- Negative Scenarios: Validate how the application handles invalid inputs, incorrect sequences, or error states.
- Boundary Cases: Include tests for limits, edge conditions, and unusual data.
Expanding coverage ensures the suite catches real-world issues rather than just expected behavior.
Step 4: Integrate Automation Smartly
Automation is key for stability, especially in CI/CD pipelines:
- Prioritize Critical Tests: Run essential tests first to catch failures early.
- Parallel Execution: Use tools like Selenium Grid with Kubernetes to run tests concurrently across browsers and environments, reducing execution time.
- Retry Logic: Implement retries for transient failures to filter out environment-induced flakiness while still flagging genuine issues.
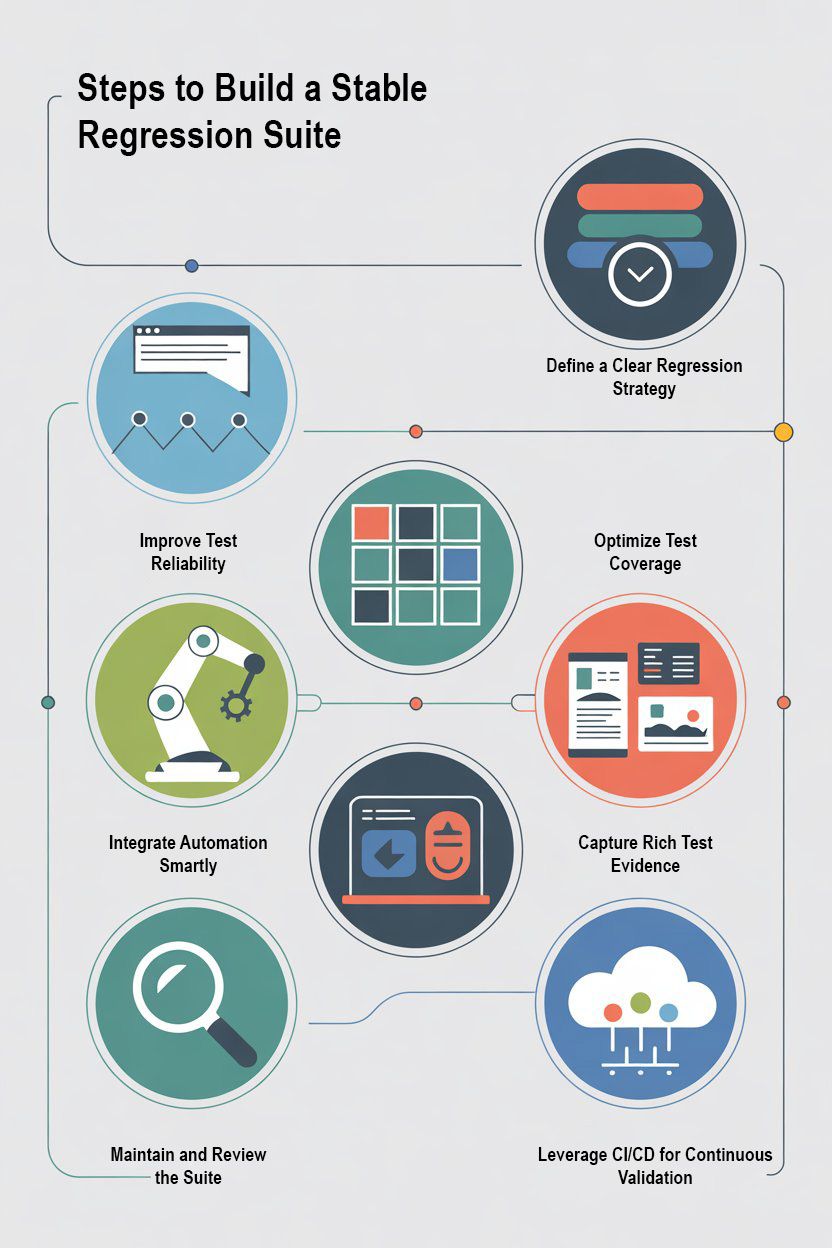
Step 5: Capture Rich Test Evidence
Reliable regression tests need actionable evidence:
- Screenshots and Videos: Capture failures visually for developers.
- HAR Files and Logs: Record network activity and application logs to aid debugging.
- Centralized Evidence Repository: Store artifacts in a single location for easy access and historical tracking.
Rich evidence reduces time spent reproducing defects and increases confidence in automated test results.
Step 6: Maintain and Review the Suite
A regression suite is not static; it requires continuous maintenance:
- Periodic Review: Remove obsolete tests, consolidate duplicates, and update tests for UI or workflow changes.
- Analyze Failures: Track flaky or unstable tests and either fix or isolate them.
- Metrics and Reporting: Monitor pass/fail rates, test execution time, and defect detection trends to identify gaps and optimize coverage.
Step 7: Leverage CI/CD for Continuous Validation
Integrating the regression suite into CI/CD pipelines ensures continuous feedback and early defect detection:
- Run Smoke Tests Per Commit: Catch critical defects before they propagate.
- Full Regression Pre-Release: Validate end-to-end functionality before pushing to production.
- Automated Notifications: Provide stakeholders with detailed results, evidence, and defect reports in real-time.
Real-World Impact
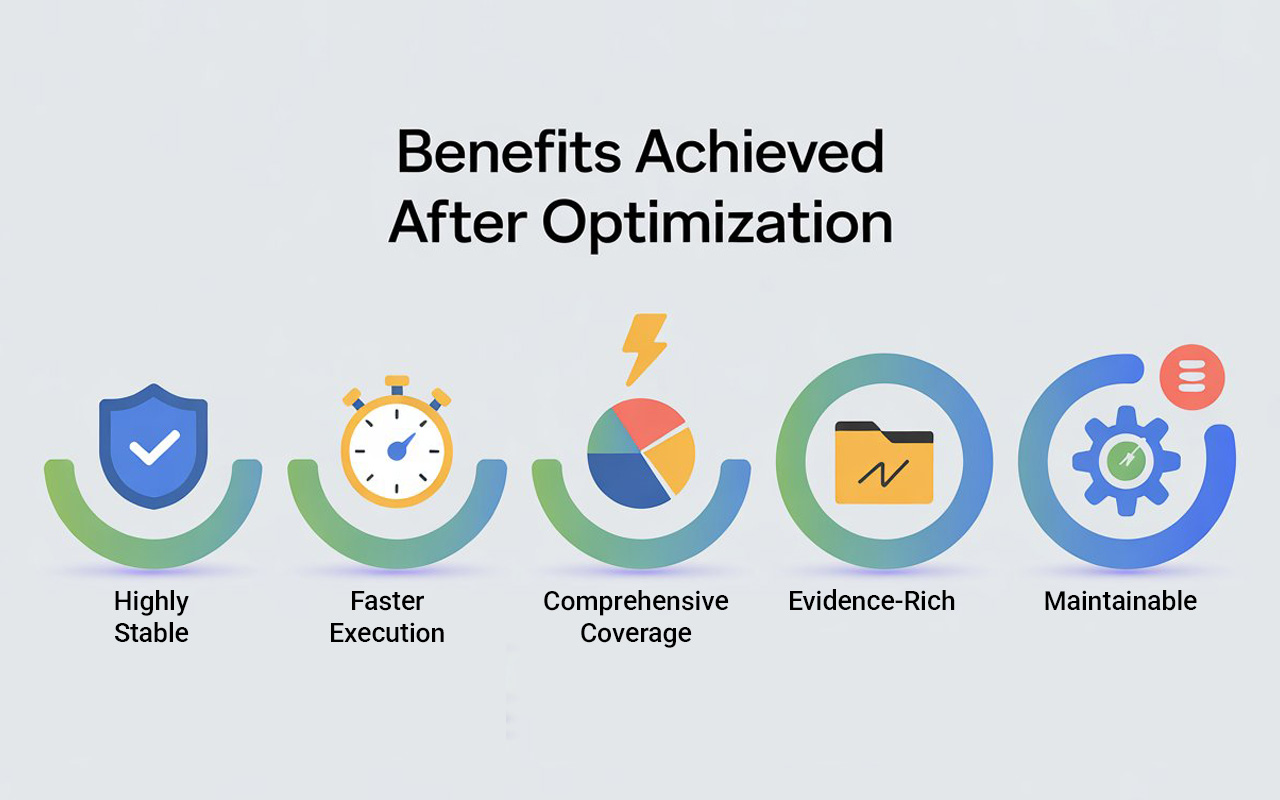
By implementing these strategies, our regression suite became:
- Highly Stable: Flaky test rates dropped dramatically, and builds were more reliable.
- Faster: Parallel execution and optimized tests reduced regression cycles from hours to under 45 minutes.
- Comprehensive: Positive, negative, and edge-case scenarios are all covered, reducing production defects.
- Evidence-Rich: Developers can quickly reproduce and fix defects using screenshots, videos, and logs.
- Maintainable: Regular review and centralized test data make it easy to update tests as the application evolves.
From my perspective, a stable regression suite doesn’t just catch bugs—it empowers the entire team, builds confidence in CI/CD pipelines, and enables faster, more predictable releases.
Conclusion
A stable QA regression suite is a strategic asset, not just a collection of tests. By improving reliability, optimizing coverage, capturing rich evidence, and integrating with CI/CD pipelines, QA teams can ensure consistent quality across releases.
From my experience, investing in stability is worth every effort. It reduces noise, accelerates feedback, prevents regressions, and empowers QA to focus on high-value testing rather than firefighting failures.
For any SDET or QA team looking to future-proof their process, the message is clear: build a regression suite that is stable, reliable, and comprehensive—it’s the backbone of quality software delivery.
FAQs
Q1. What is a QA regression suite?
A QA regression suite is a collection of automated and manual tests that verify existing functionality still works after code changes. It acts as a safety net to catch defects before they reach production, especially during frequent releases.
Q2. What makes a regression suite stable?
A stable regression suite has reliable tests that rarely fail due to timing or environment issues, uses clean test data, runs in predictable environments, and is reviewed regularly to remove obsolete or duplicate tests. Teams can trust its results in every CI/CD run.
Q3. How can I reduce flaky test automation in my regression suite?
To reduce flakiness, replace hard-coded sleeps with explicit waits, isolate tests so they don’t depend on each other, stabilize test data, and add retry logic only for known transient issues like network delays or environment hiccups.
Q4. Which tests should go into smoke, critical and full regression?
Smoke tests should cover the most essential flows like login and basic navigation. Critical tests focus on high-risk business paths such as payments or core transactions. Full regression includes broader end-to-end and edge-case scenarios that validate overall system health before a major release.
Q5. How does CI/CD help keep regression suites stable?
Integrating the regression suite into CI/CD ensures tests run consistently on every commit or build. This provides fast feedback, catches issues early, and prevents unstable changes from moving forward. Over time, CI/CD regression testing exposes flaky tests and gaps in coverage so teams can fix them.
Q6. Why is capturing evidence important in regression testing?
Capturing screenshots, videos, logs and HAR files makes it easier for developers to understand failures without reproducing every issue manually. Evidence-rich regression tests speed up debugging, reduce back-and-forth between QA and dev, and increase confidence in automated results.
We Also Provide Training In:
- Advanced Selenium Training
- Playwright Training
- Gen AI Training
- AWS Training
- REST API Training
- Full Stack Training
- Appium Training
- DevOps Training
- JMeter Performance Training
Author’s Bio:

Content Writer at Testleaf, specializing in SEO-driven content for test automation, software development, and cybersecurity. I turn complex technical topics into clear, engaging stories that educate, inspire, and drive digital transformation.
Ezhirkadhir Raja
Content Writer – Testleaf







