Introduction: Why Cybersecurity Skills Are Being Redefined
Cybersecurity is no longer just about firewalls and antivirus tools.
By 2026, cyber threats will be faster, smarter, and more automated than ever before.
Organizations are already shifting their expectations. They are not hiring people who only know tools. They are hiring professionals who understand systems, risk, automation, and decision-making.
If your cybersecurity skillset still looks the same as it did in 2022, it will not hold up in 2026.
This guide breaks down the 10 essential cybersecurity skills you must master—not based on theory, but on how real-world security teams operate today.
1. Networking Fundamentals (The Skill Most Beginners Skip)
Every cyber attack travels through a network.
If you do not understand:
- How data packets move
- How DNS, TCP/IP, and HTTP work
- How internal and external networks differ
You cannot effectively detect or stop attacks.
Strong networking knowledge allows you to:
- Identify suspicious traffic
- Understand attack paths
- Respond faster during incidents
This is the foundation of all cybersecurity roles.
You Might Also Like: playwright interview questions
2. Operating Systems & Linux Mastery
Most enterprise servers run on Linux.
Most security tools are built for Linux.
You must be comfortable with:
- Linux command line
- File permissions
- Process management
- System logs
This skill directly impacts your ability to perform investigations, run tools, and secure environments.
3. Threat Detection & Incident Response Thinking
Modern cybersecurity is about response speed, not just prevention.
Professionals must know:
- How to identify security incidents
- How to analyze logs and alerts
- How to contain threats before damage spreads
Organizations value people who can think clearly under pressure and follow structured incident response processes.
4. Cloud Security (Now a Core Skill, Not Optional)
Most businesses operate on cloud platforms.
Cybersecurity professionals must understand:
- Shared responsibility models
- Cloud access control
- Misconfiguration risks
- Identity-based security
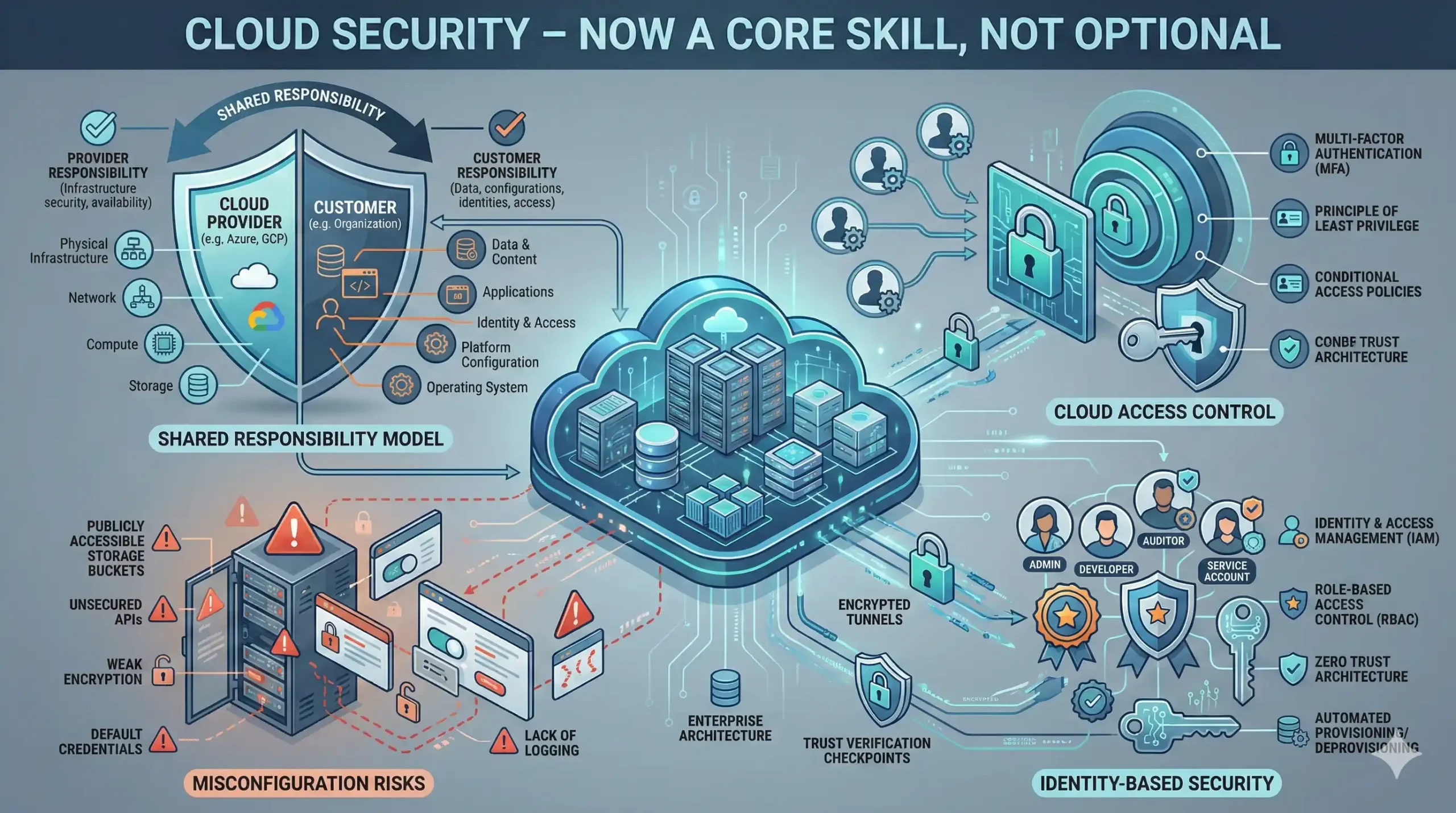
Cloud security skills directly influence hiring decisions in 2026.
5. Automation & Scripting for Security Efficiency
Manual security does not scale.
Security teams expect professionals to:
Automation reduces response time and human error—two major causes of security failures.
Don’t Miss Out: manual testing interview questions
6. Risk Assessment & Security Decision-Making
Cybersecurity is not just technical—it is strategic.
Professionals must:
- Evaluate business impact
- Prioritize vulnerabilities
- Communicate risk clearly
This skill separates entry-level analysts from trusted security advisors.
7. Security Tools & SIEM Awareness
Tools do not replace thinking—but they amplify it.
You should understand:
- SIEM platforms
- Log correlation
- Alert tuning
- Monitoring workflows
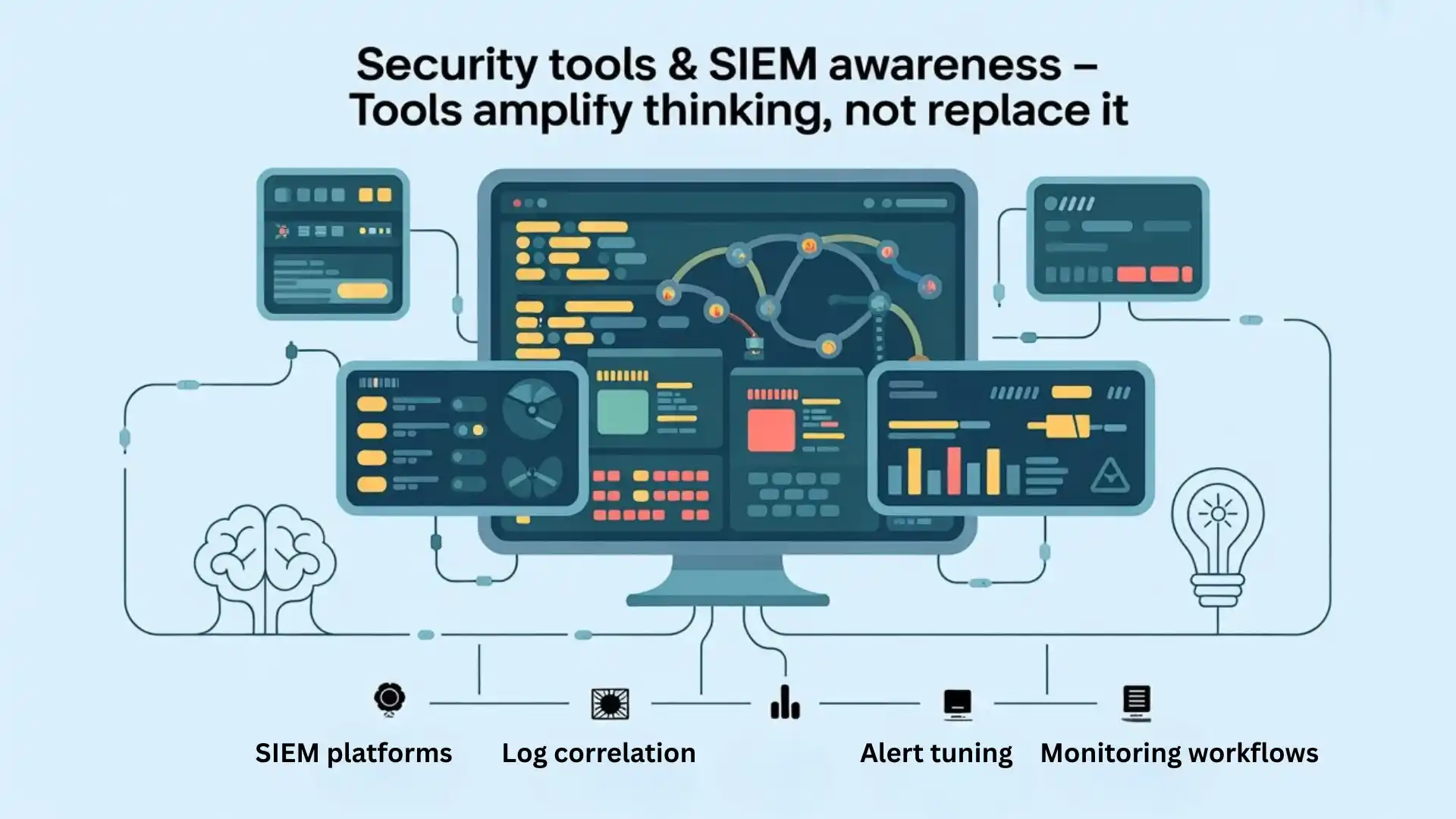
Hiring managers value candidates who know why a tool is used, not just how to click buttons.
8. Compliance, Governance & Security Standards
Security exists within rules.
Understanding:
- Security policies
- Compliance basics
- Industry standards
helps organizations avoid legal and financial damage.
This knowledge becomes critical as you move into senior roles.
See Also: automation testing interview questions
9. AI-Driven Security Awareness
AI is transforming cybersecurity.
Professionals must understand:
- How AI improves threat detection
- Where AI fails
- How attackers misuse AI
You do not need to build AI models—but you must understand how AI influences modern security systems.
10. Communication & Collaboration Skills
Cybersecurity professionals do not work alone.
You must:
- Explain risks to non-technical teams
- Collaborate with developers and operations
- Document findings clearly
Strong communication increases trust and career growth.
Why These Skills Matter More in 2026
Cybersecurity roles are evolving fast.
Organizations no longer hire based on certifications alone.
They hire professionals who:
- Think system-wide
- Adapt to new threats
- Combine technical and human skills
Mastering these 10 skills ensures long-term relevance—not just your next job.
Final Takeaway: Build Skills That Outlast Tools
Tools will change.
Threats will evolve.
But core cybersecurity skills will always remain valuable.
Technologies may come and go, and security platforms may be replaced every few years, but a strong understanding of systems, risk management, automation, and clear communication never loses relevance. These are the skills that allow cybersecurity professionals to adapt quickly, make informed decisions, and respond effectively when real threats occur.
If you focus on building these fundamentals, you will stay competitive—no matter how the industry shifts in 2026 and beyond. This is especially important for beginners and career switchers who want long-term stability, not just short-term job placement. A structured Cybersecurity course online can help you strengthen these core skills through practical learning, real-world scenarios, and guided expertise, making it easier to translate knowledge into on-the-job performance.
In the end, cybersecurity success is not defined by how many tools you know, but by how well you think, adapt, and protect systems under pressure. Master the skills that outlast tools, and your career will grow with the industry, not struggle to catch up.
FAQs
1. What are the most important cybersecurity skills for 2026?
The most important cybersecurity skills for 2026 include networking fundamentals, Linux, cloud security, threat detection, automation, risk assessment, AI awareness, and strong communication skills.
2. Are cybersecurity skills more important than tools?
Yes. Tools change frequently, but core cybersecurity skills such as system understanding, risk analysis, and incident response remain essential for long-term career growth.
3. Do beginners need coding skills for cybersecurity?
Basic scripting skills are highly recommended. Coding helps automate security tasks, analyze threats, and improve efficiency in real-world security operations.
4. Is cloud security a mandatory skill for cybersecurity professionals?
Yes. Since most organizations operate in cloud environments, understanding cloud security models and misconfigurations is critical for modern cybersecurity roles.
5. Can I learn cybersecurity skills online?
Yes. A structured Cybersecurity course online can help beginners and professionals gain practical skills, hands-on experience, and industry-relevant knowledge.
We Also Provide Training In:
- Advanced Selenium Training
- Playwright Training
- Gen AI Training
- AWS Training
- REST API Training
- Full Stack Training
- Appium Training
- DevOps Training
- JMeter Performance Training
Author’s Bio:

Content Writer at Testleaf, specializing in SEO-driven content for test automation, software development, and cybersecurity. I turn complex technical topics into clear, engaging stories that educate, inspire, and drive digital transformation.
Ezhirkadhir Raja
Content Writer – Testleaf